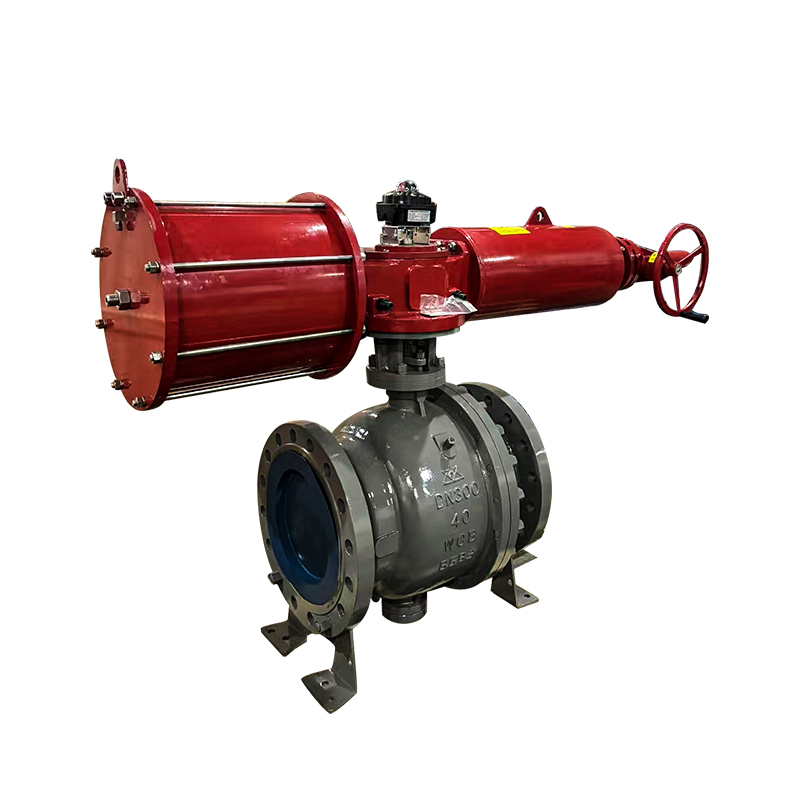
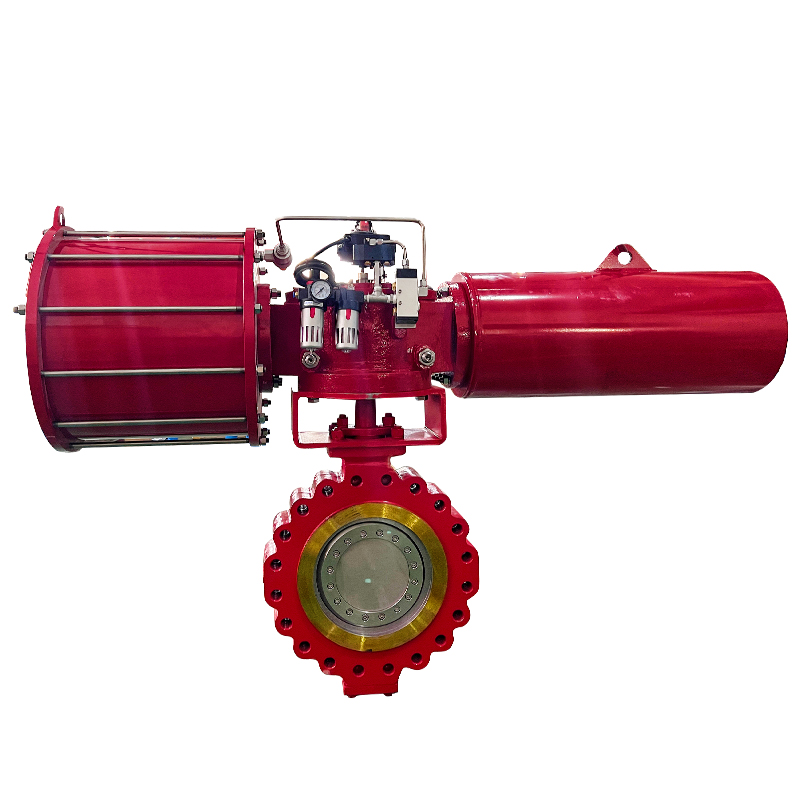
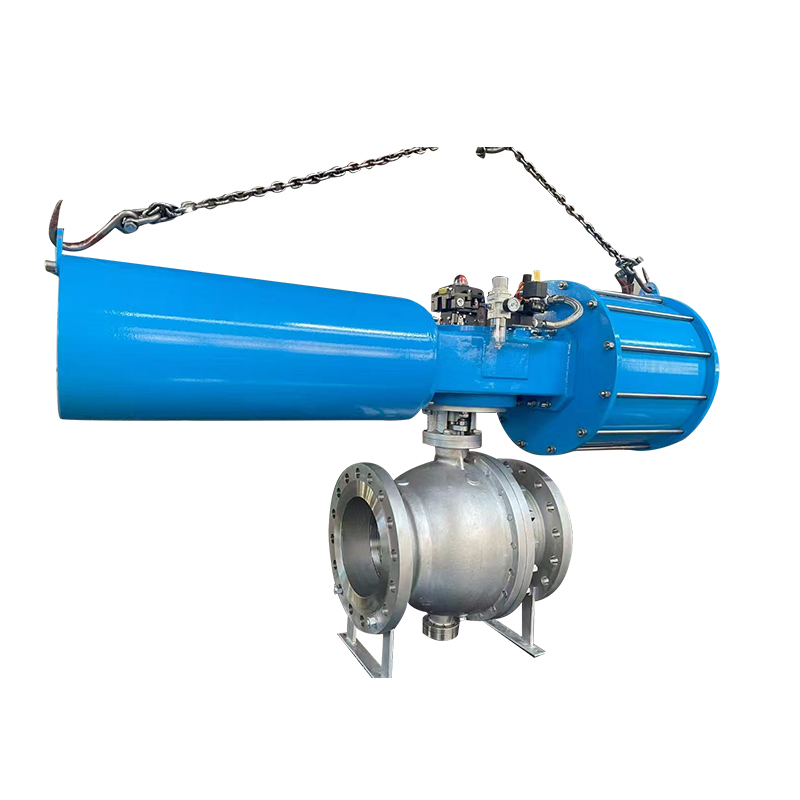
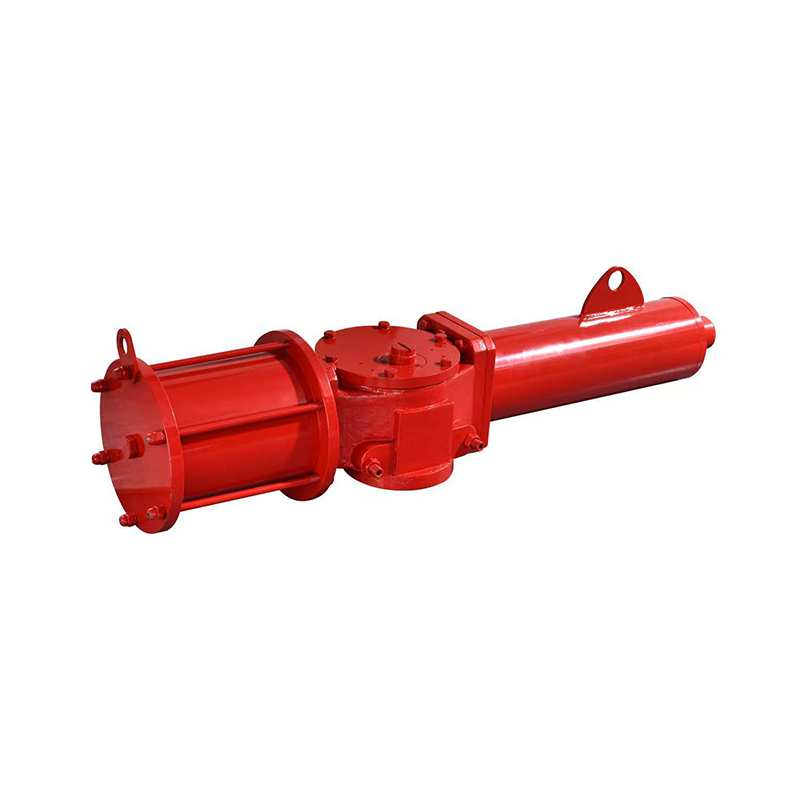
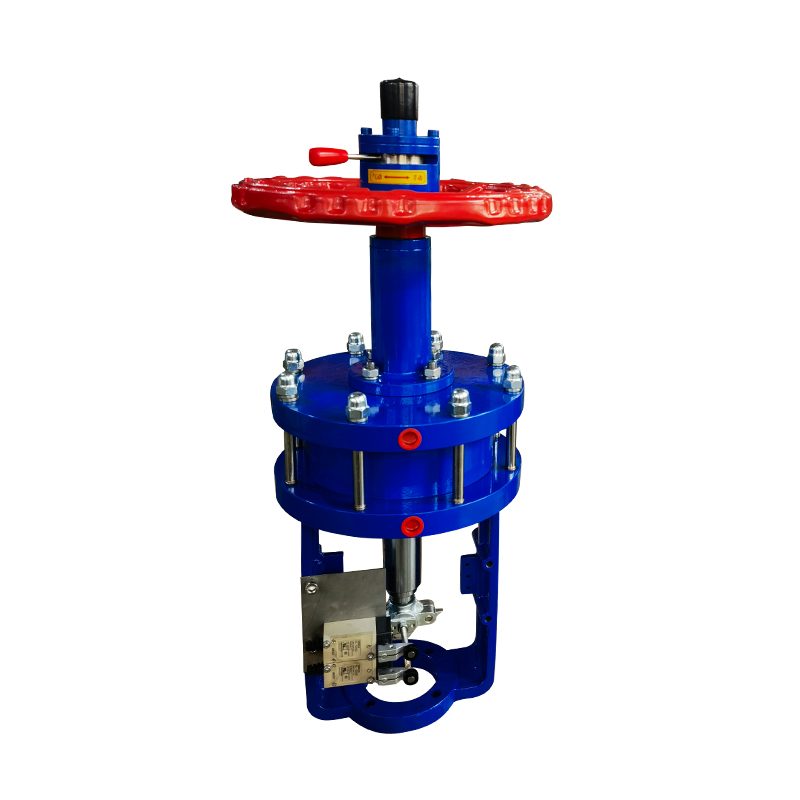
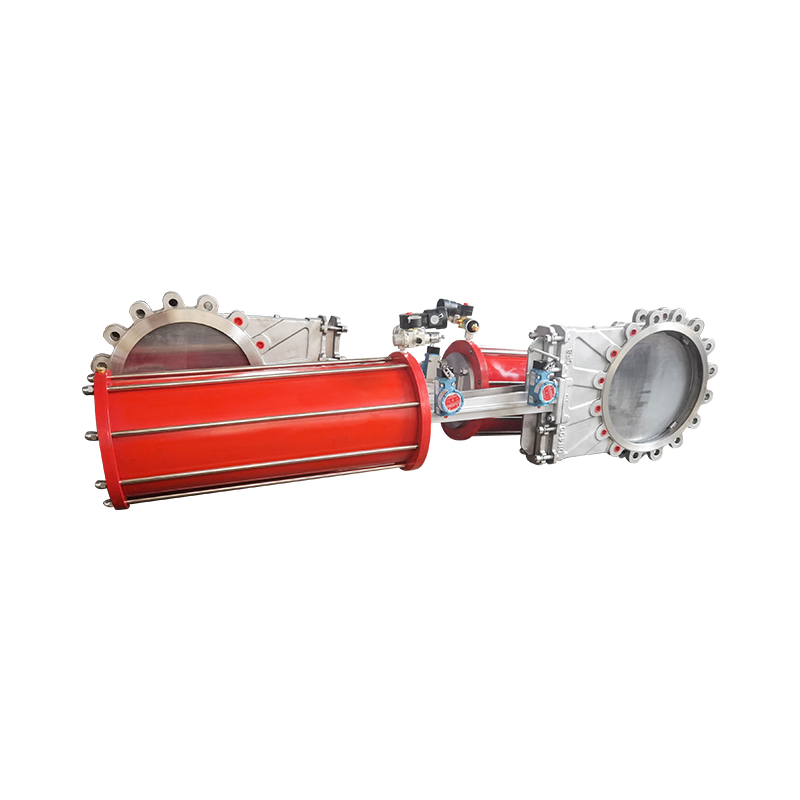
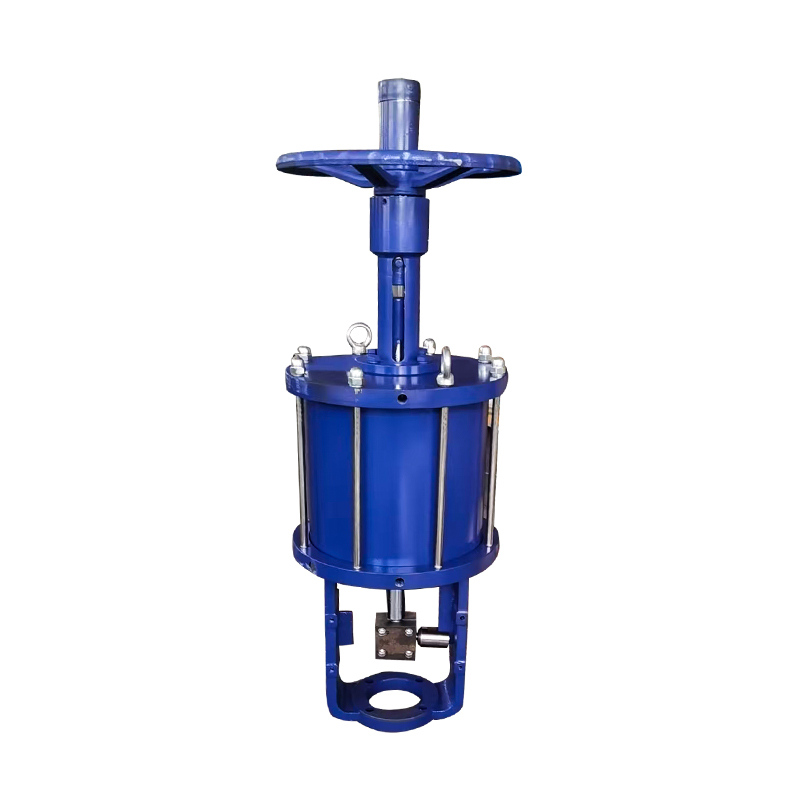
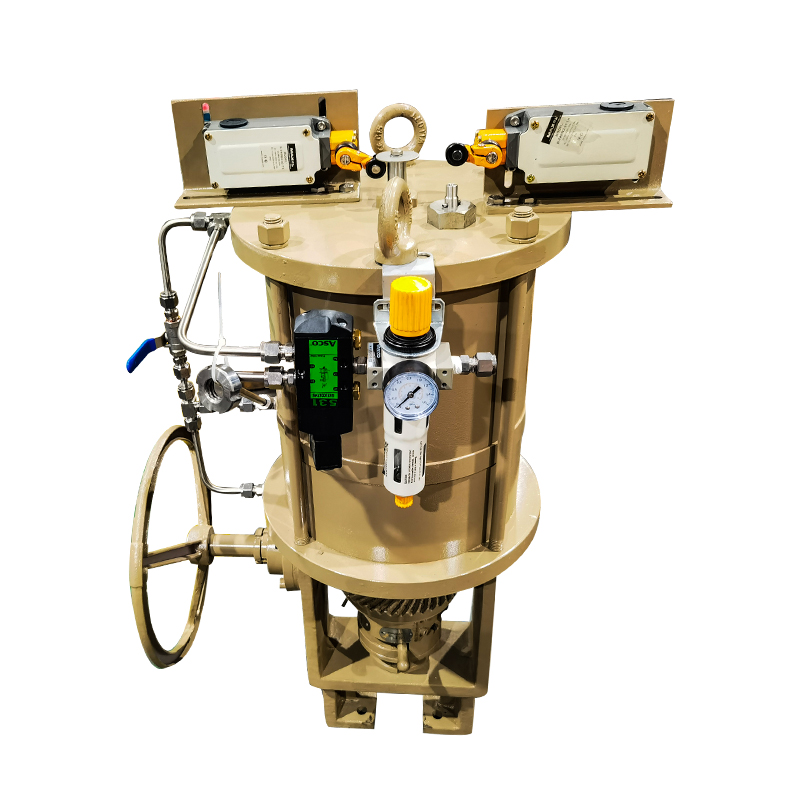
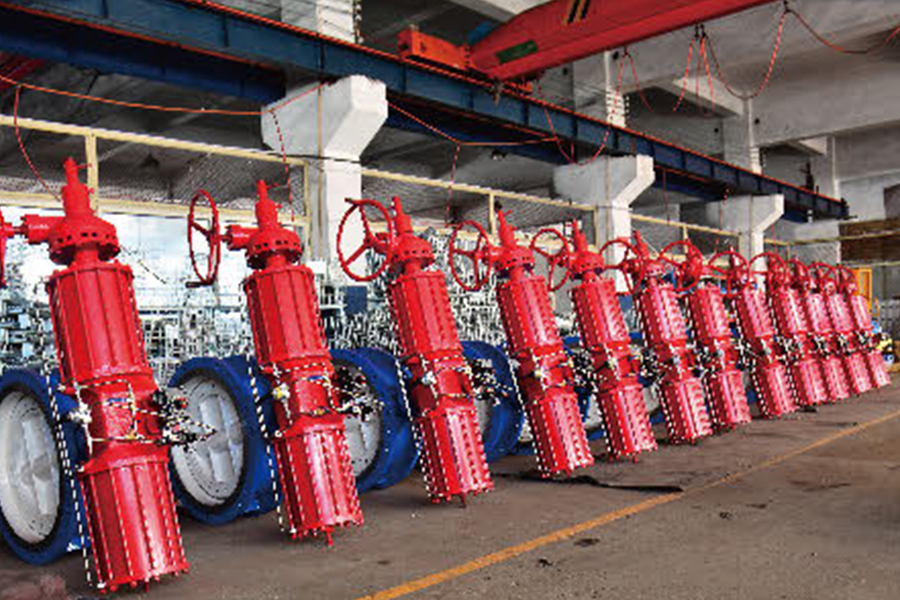
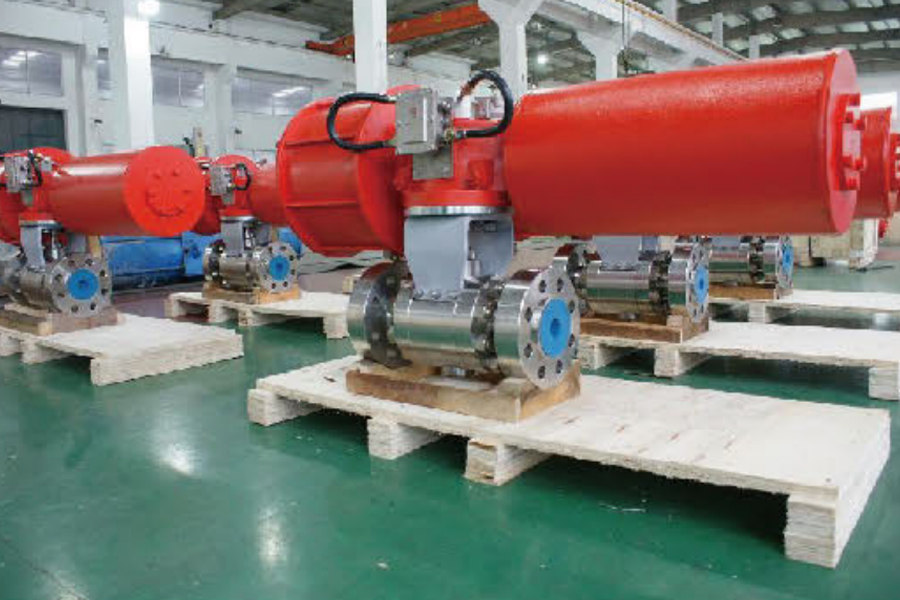
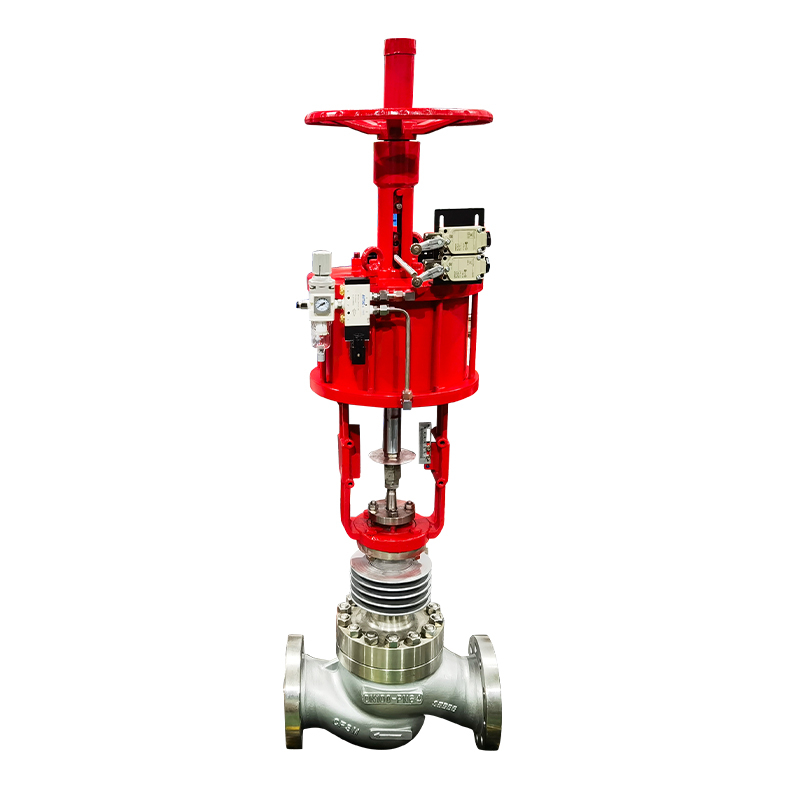
Valves play a crucial role in regulating the flow of various fluids in industrial systems. Among them, the diaphragm valve is commonly used in applications requiring flow regulation, such as in the pharmaceutical, food, and chemical industries. However, in some applications, the diaphragm valve may not meet the specific operational needs, particularly in high-demand environments or systems that require more precision and automation. This is where the replacement of diaphragm valves with pneumatic actuators comes into play, offering several advantages in terms of efficiency, control, and durability.
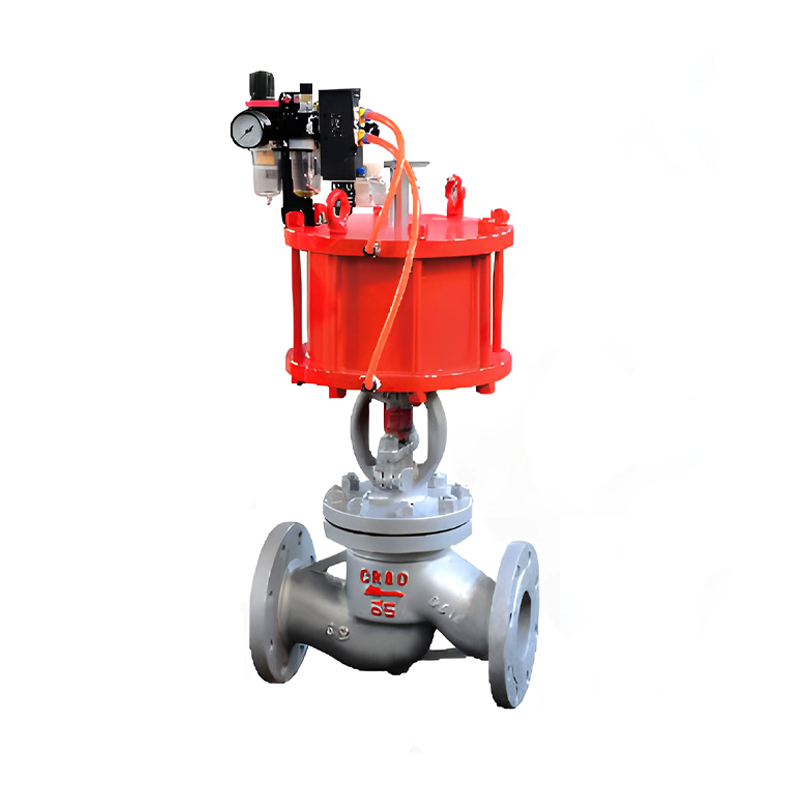

A diaphragm valve operates by using a flexible diaphragm that is pressed against a seat to control flow. While diaphragm valves are good for throttling and shutoff, they have limitations when it comes to handling high-pressure systems, heavy-duty applications, or automation needs. In these scenarios, a pneumatic actuator can be a more efficient and reliable choice.
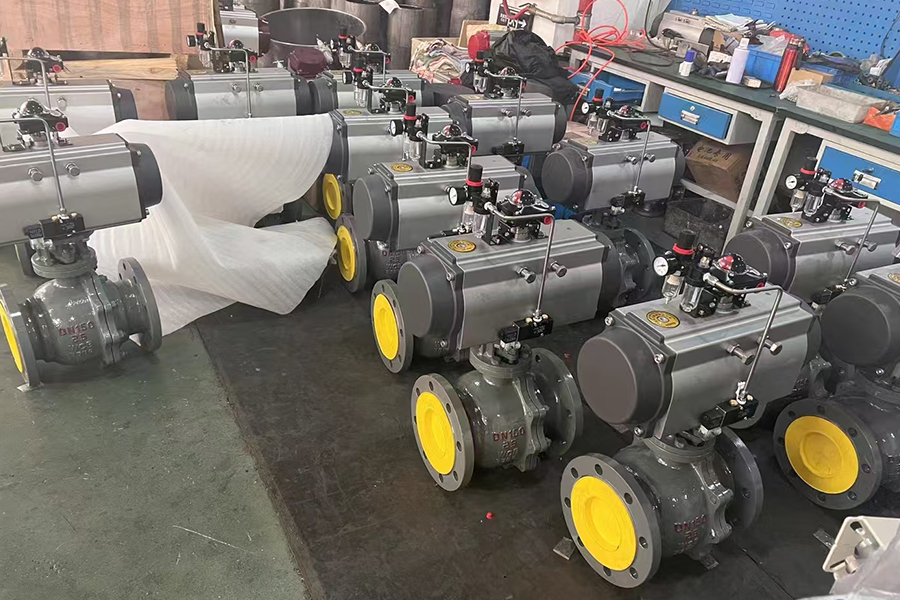
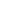
The replacement of diaphragm valves with pneumatic actuators offers several benefits. Pneumatic actuators use compressed air to move the valve's internal mechanism, making them faster and more precise than manual or diaphragm-based systems. This allows for better control over the flow of fluids, particularly in automated systems where real-time adjustments are essential. Additionally, pneumatic actuators are capable of handling higher pressure ranges, making them suitable for industrial applications requiring more robust and high-performance valves.
Compact pneumatic actuators are widely used in industries where automated control of fluid or gas flow is required. These actuators are designed to be smaller and more efficient compared to traditional pneumatic actuators, making them ideal for applications where space is limited. However, like all industrial equipment, compact pneumatic actuators are exposed to harsh operating conditions, including exposure to moisture, corrosive chemicals, and high-pressure systems. To maintain their functionality, longevity, and reliability, anti-corrosion treatment becomes a critical aspect of actuator design and maintenance.
Anti-corrosion treatment refers to the application of protective coatings or processes that prevent the actuator's metal parts from rusting or deteriorating due to exposure to corrosive elements. Pneumatic actuators are often exposed to environments that contain water, salt, or chemicals, all of which can contribute to corrosion over time. Without proper treatment, corrosion can compromise the actuator's performance, failure, increased maintenance costs, and even system downtime.
There are various methods of anti-corrosion treatment applied to compact pneumatic actuators. One common method is the use of epoxy coatings, which are applied to the actuator's components, particularly the housing and valve body. Epoxy coatings create a protective barrier between the actuator and the environment, preventing moisture and corrosive chemicals from coming into contact with the metal surface. These coatings are highly durable and can withstand a wide range of temperatures and environmental conditions.
Another effective anti-corrosion treatment is galvanization, which involves coating the metal components with a layer of zinc. This zinc layer acts as a sacrificial anode, corroding before the underlying metal can degrade. Galvanization is particularly useful in preventing rust and is widely used for outdoor or marine applications.
Anodizing is another popular method, particularly for aluminum-based actuators. This electrochemical process thickens the oxide layer on the metal surface, improving resistance to wear, corrosion, and other environmental stresses. Anodized surfaces also offer better aesthetic appeal and can provide additional insulation properties.