-
 [email protected]
[email protected]
-
 +86-13566253888
+86-13566253888

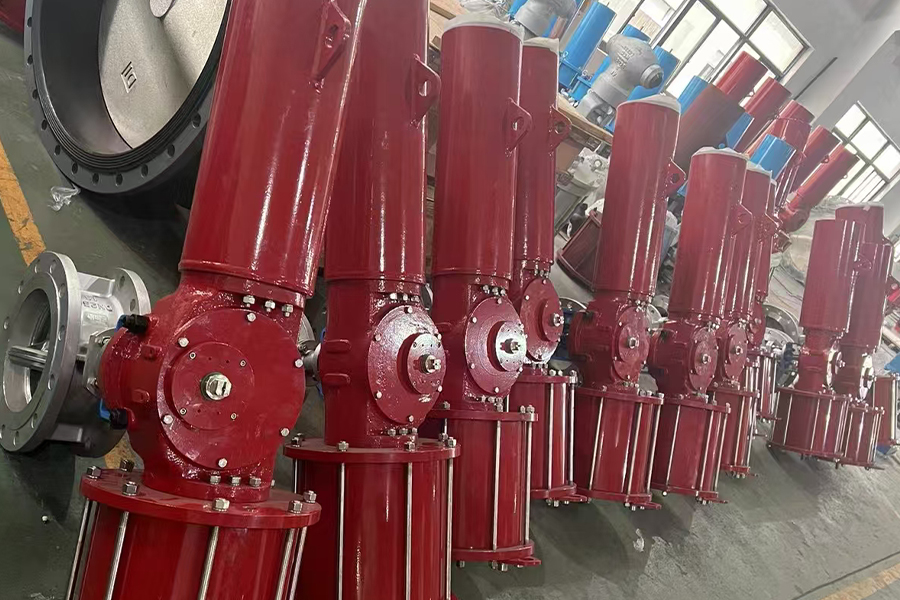
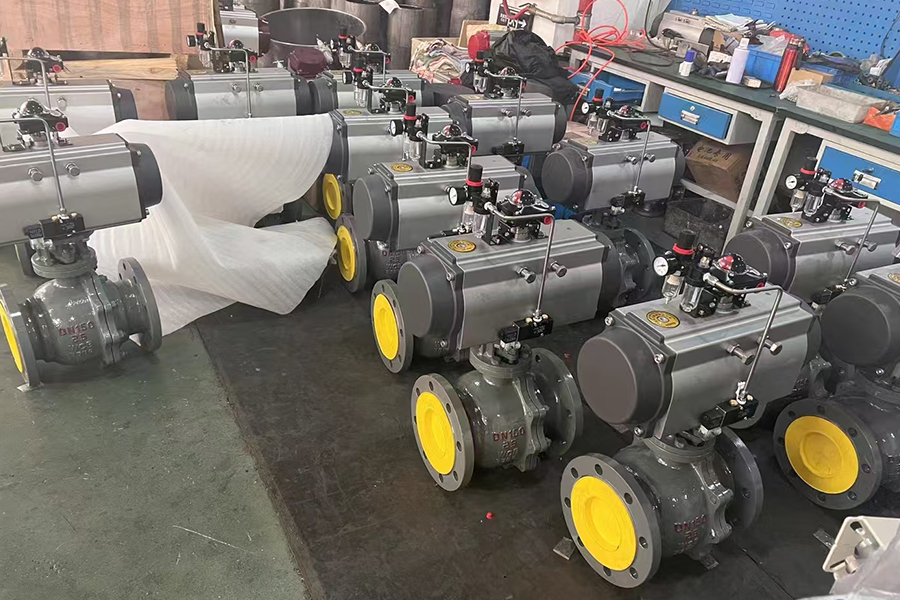
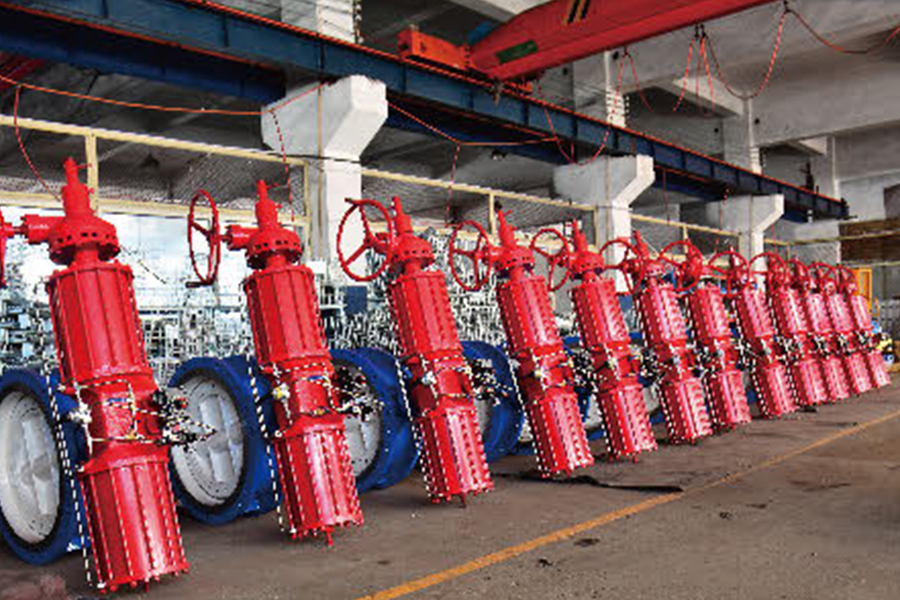
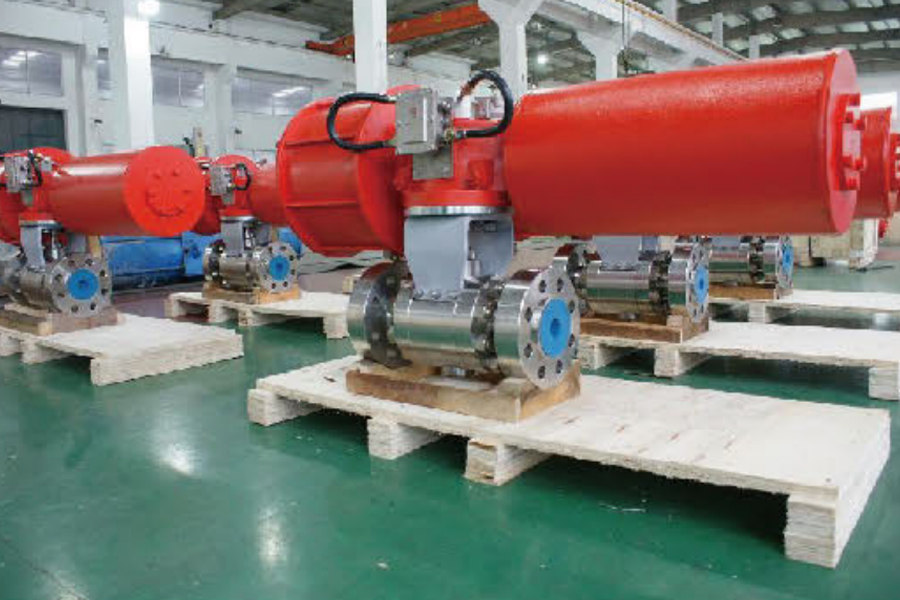
A pneumatic gate valve is a highly efficient flow control device widely used in various industries for managing the movement of fluids, gases, and semi-solids. This type of valve operates through pneumatic actuators, which utilize compressed air to control the opening and closing mechanism. Unlike manual or electrically operated gate valves, pneumatic gate valves offer enhanced automation, rapid response times, and minimal manual intervention. Their ability to provide a reliable, tight seal makes them ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications, ensuring smooth and uninterrupted operations.
Structurally, a pneumatic gate valve consists of a gate or wedge that moves up and down within the valve body to regulate the flow of media. It is designed to function in either a fully open or fully closed position, making it perfect for applications where precise shutoff is required. The material composition of these valves, such as stainless steel, carbon steel, or specialized alloys, ensures durability and resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for harsh environments.
Applications
Pneumatic gate valves are extensively utilized across multiple industries due to their reliability and efficiency. Some of the primary applications include:
Oil and Gas Industry – These valves are used in pipeline systems for the transportation of crude oil, natural gas, and refined petroleum products. Their ability to handle high-pressure environments ensures safety and efficiency in fluid control operations.
Chemical Processing – Pneumatic gate valves are employed in chemical plants where the handling of corrosive and hazardous substances requires highly durable and leak-proof valves. They are used in processes such as mixing, storage, and transfer of chemicals.
Water Treatment Facilities – These valves play a crucial role in controlling the flow of water and wastewater in municipal and industrial treatment plants. Their capability to provide a secure seal ensures contamination-free processing.
Power Generation – In thermal and nuclear power plants, pneumatic gate valves regulate the flow of steam, cooling water, and other essential fluids, contributing to the safe and efficient operation of turbines and boilers.
Food and Beverage Industry – Ensuring hygiene and preventing contamination are critical in food processing plants. Pneumatic gate valves help in controlling the flow of liquids, dairy products, and other consumables, meeting stringent industry standards.
Mining and Metallurgy – These valves are used in slurry transportation, dewatering systems, and material processing applications where heavy-duty performance is required to withstand abrasive and high-pressure conditions.
Services
To ensure optimal performance and longevity of pneumatic gate valves, various services are offered by manufacturers and service providers. These services include:
Customization – Tailoring valves according to specific operational requirements, including size, material, pressure rating, and actuation mechanisms.
Installation and Commissioning – Providing professional installation services to ensure proper integration of the valve within the system, minimizing risks of leakage or operational failures.
Maintenance and Repair – Regular inspection, lubrication, and replacement of worn-out components help in maintaining the efficiency of the valve over time.
Technical Support and Consultation – Expert advice on valve selection, troubleshooting, and performance optimization to maximize operational efficiency.
Upgrades and Retrofitting – Enhancing existing valve systems with advanced pneumatic actuation technology to improve automation and reliability.
Pneumatic gate valves are essential components in fluid control systems, offering precision, durability, and efficiency across various industries. By leveraging professional services, businesses can ensure the longevity and optimal performance of these critical components.
Establishment
Project Cases






