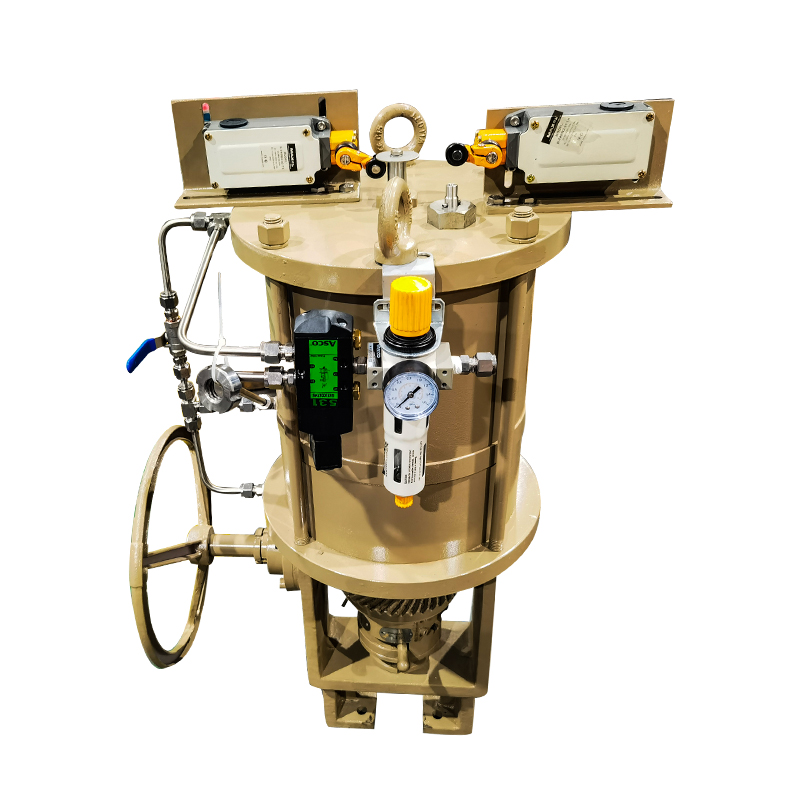
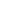
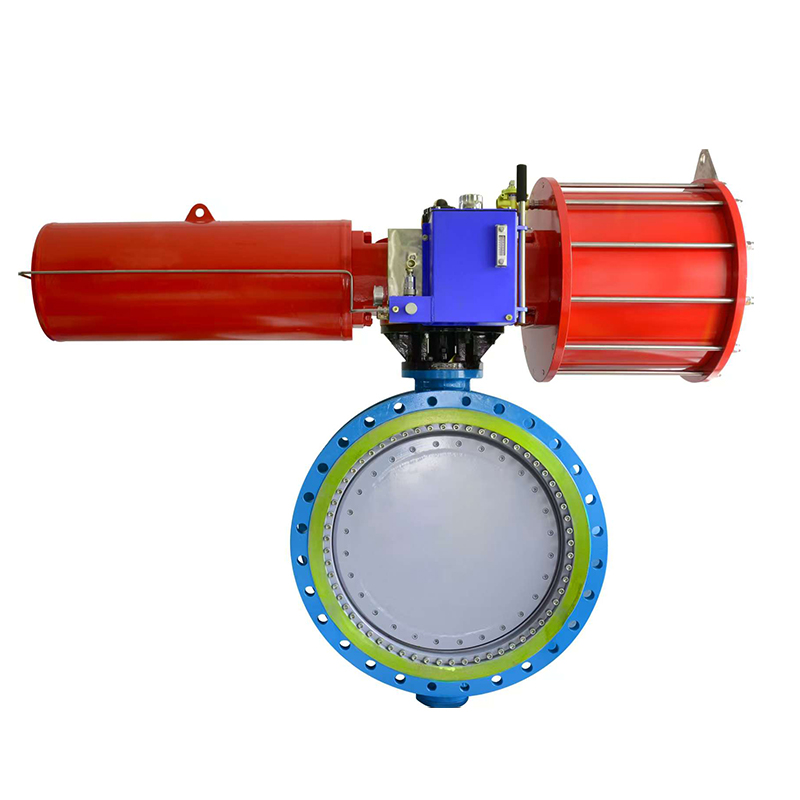
Double acting pneumatic valves play an important role in automated fluid control systems, offering precise and consistent actuation in both directions. These valves rely on compressed air to move the actuator both to open and close the valve, which makes them effective in applications that demand high control and fast response. To ensure long-term reliability and efficiency, regular maintenance of a double acting pneumatic valve is necessary.
One of the main maintenance tasks for a double acting pneumatic valve is inspection of the air supply system. Since these valves depend entirely on compressed air to function, any issue in the air line can lead to poor performance. It is important to check for air leaks, pressure drops, or contamination in the air supply. Filters and regulators should be examined regularly and cleaned or replaced when necessary. Dirty or moist air can cause internal wear, so maintaining clean, dry air is essential for protecting the valve components.
Lubrication is another important part of maintaining a double acting pneumatic valve. While some valves are designed to be maintenance-free or include pre-lubricated components, others require periodic lubrication of internal seals, pistons, or shafts. Using the correct type of lubricant is critical, as the wrong formulation can damage seals or attract dust and debris. Always refer to the manufacturer's guidelines when selecting a lubricant and follow the recommended schedule to ensure consistent performance.
Seals and gaskets inside a double acting pneumatic valve are subject to wear over time due to constant motion and pressure changes. Regular inspection for signs of wear, cracking, or deformation is important. Replacing worn seals prevents air leakage and maintains proper valve function. In high-cycle or harsh environment applications, these components may need to be inspected more frequently to avoid unplanned downtime.
The actuator itself should also be checked periodically. This includes examining the cylinder walls, pistons, and end caps for signs of wear, corrosion, or physical damage. Loose or misaligned actuator components can result in sluggish or incomplete valve movement, which could affect the entire system. In addition, mounting brackets and fasteners should be tightened and aligned to prevent vibration or mechanical stress.
Testing valve function is a simple but essential step in regular maintenance. By cycling the double acting pneumatic valve manually or through the control system, operators can observe whether the valve opens and closes fully and responds correctly to signals. Any delay, hesitation, or partial movement should be investigated immediately. Such issues may indicate internal wear, air supply problems, or control signal inconsistencies.
Cleaning the exterior of the valve and actuator assembly helps reduce the risk of dirt and debris entering the system. In environments where dust, chemicals, or moisture are present, it's especially important to prevent buildup on external surfaces. This not only protects the valve but also ensures that nameplates and identification labels remain visible for future maintenance work.
Keeping accurate records of maintenance activities is useful for identifying patterns of wear or failure. Tracking how often seals are replaced, air filters are cleaned, or actuators are serviced can help predict when future maintenance will be needed and allow for better planning. This kind of preventative maintenance approach helps ensure that the double acting pneumatic valve remains reliable throughout its service life.
Regular inspection, lubrication, cleaning, and functional testing are all essential maintenance practices for a double acting pneumatic valve. By paying attention to these areas and addressing small issues early, operators can extend the valve's service life and support safe and efficient operation in their fluid control systems.