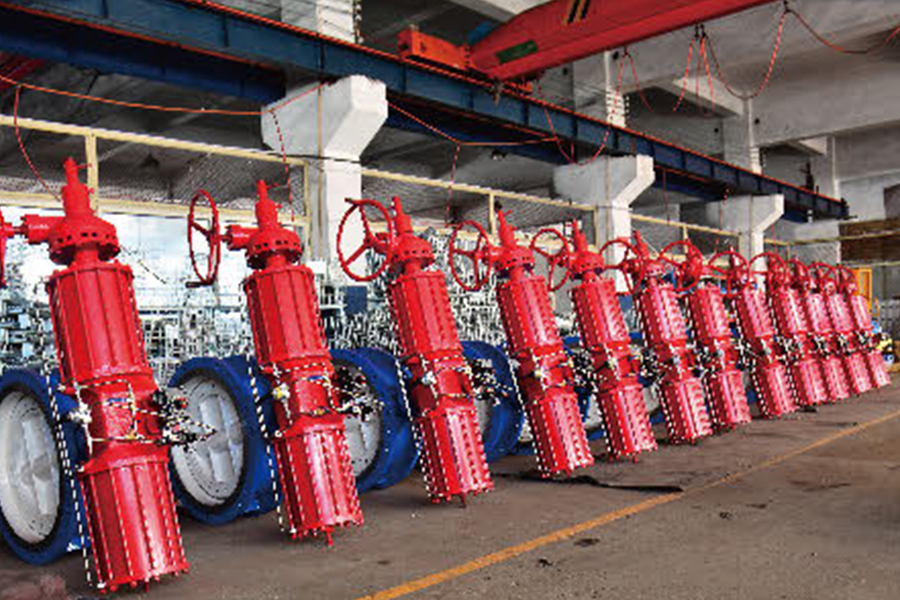
Actuators are essential components in fluid control systems, translating energy into mechanical motion to operate valves. Among the many types available, Scotch yoke actuators and linear pneumatic actuator valves each serve specific functions based on design and application requirements. This article explores the key characteristics of the Scotch yoke type actuator and identifies where linear pneumatic actuator valves are commonly used.
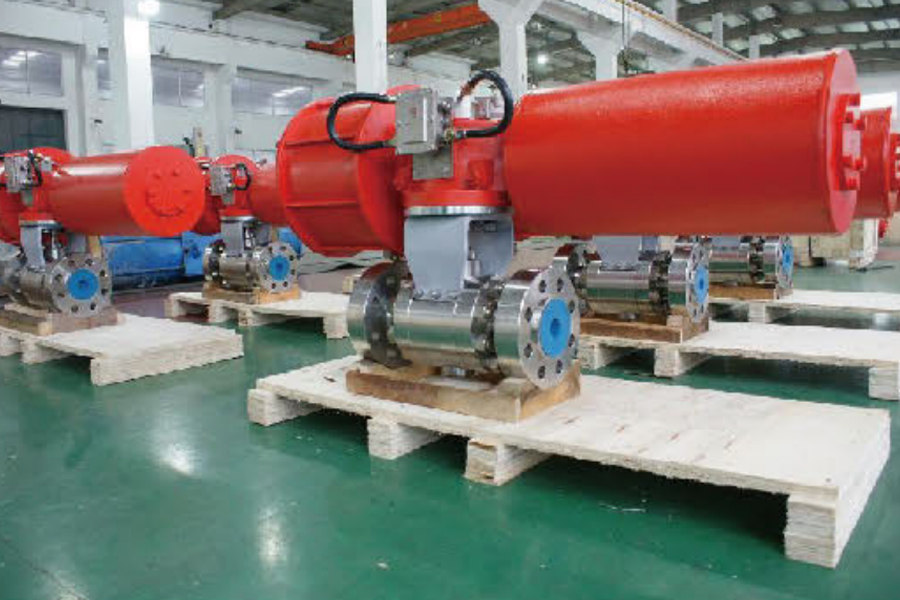

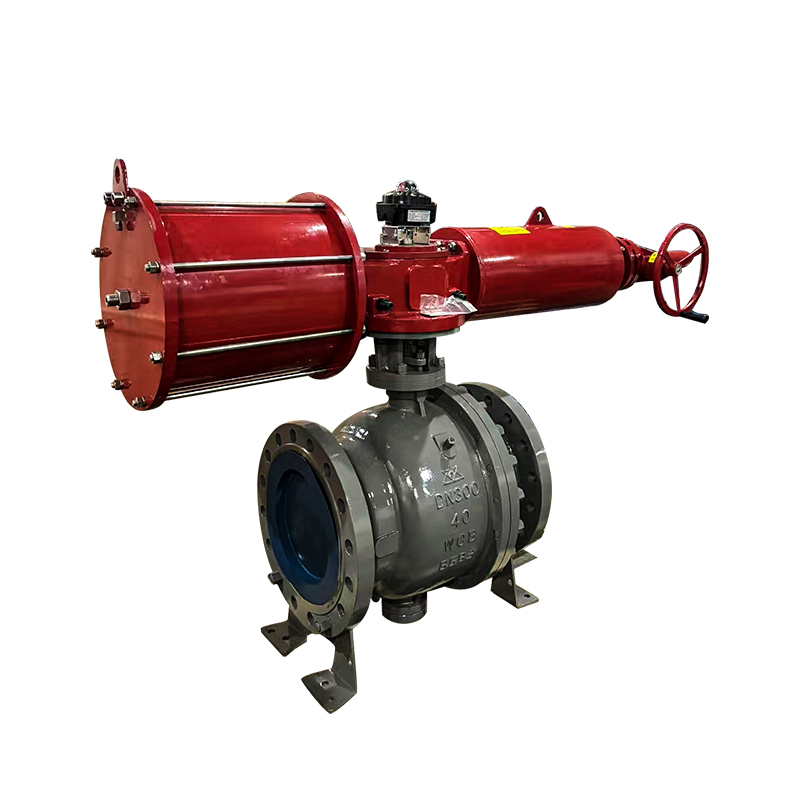
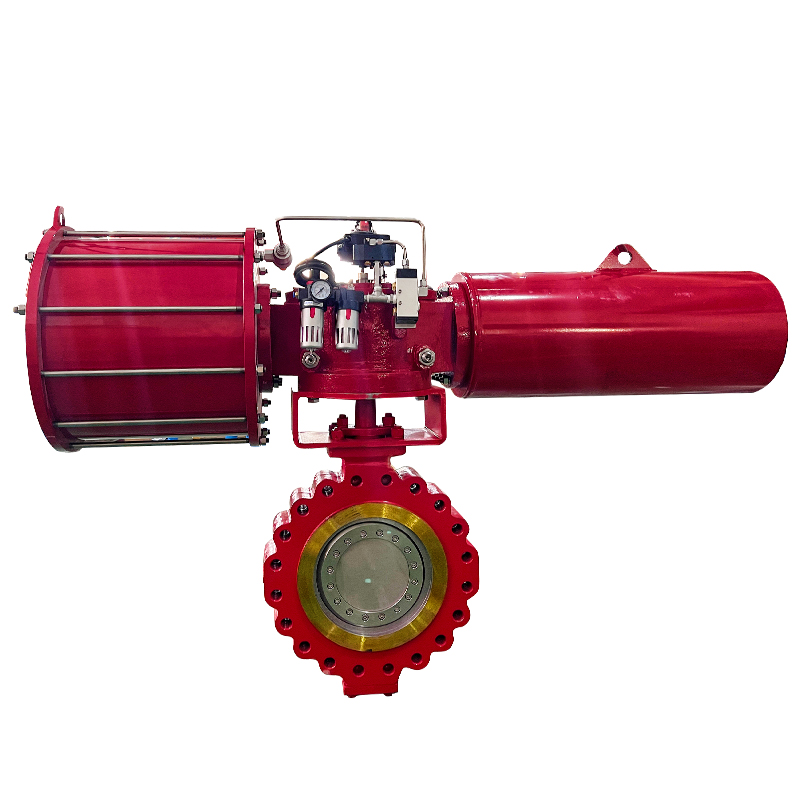
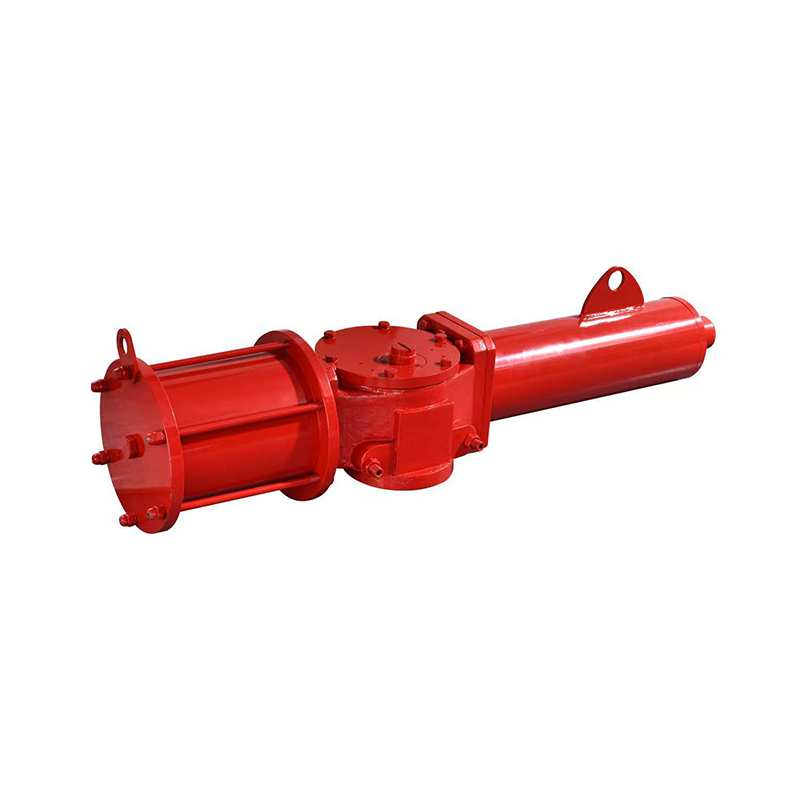
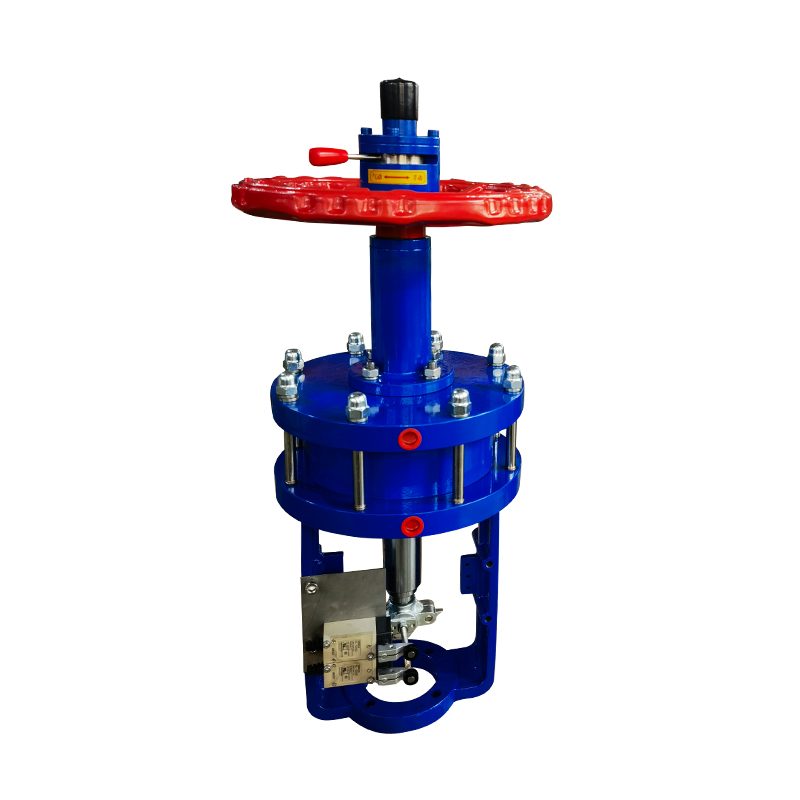
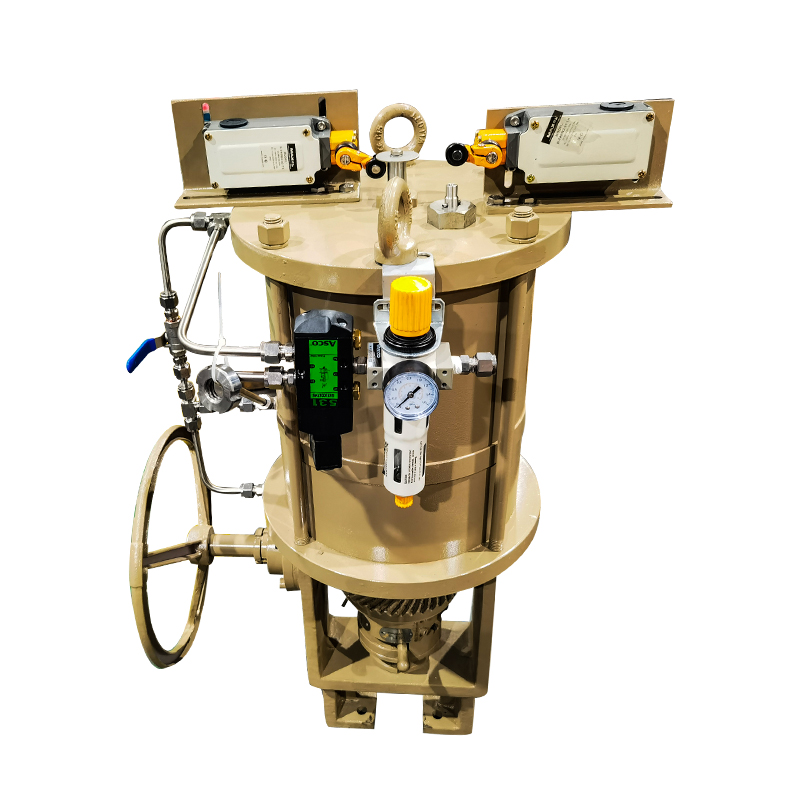
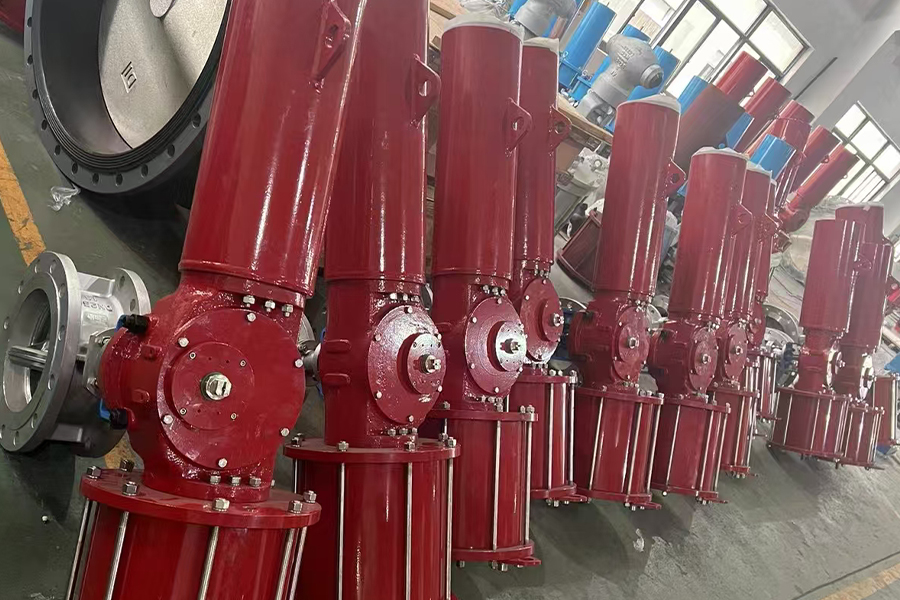
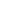
The Scotch yoke type actuator is a mechanical device used to convert the linear motion of a piston into the rotational movement required to operate quarter-turn valves, such as ball or butterfly valves. It is named after its distinctive yoke mechanism, which guides the piston's motion to create torque output.
One of the notable characteristics of a Scotch yoke type actuator is its torque profile. Unlike rack and pinion actuators that deliver consistent torque throughout the stroke, Scotch yoke actuators generate higher torque at the beginning and end of the stroke. This is especially beneficial for valves that require a strong initial force to break from their seated position and to reseat securely when closing.
Another important characteristic is mechanical simplicity. The Scotch yoke design uses fewer moving parts compared to some alternatives, which can result in a more compact and cost-effective construction. This also contributes to reduced wear and potentially longer service life, depending on the application.
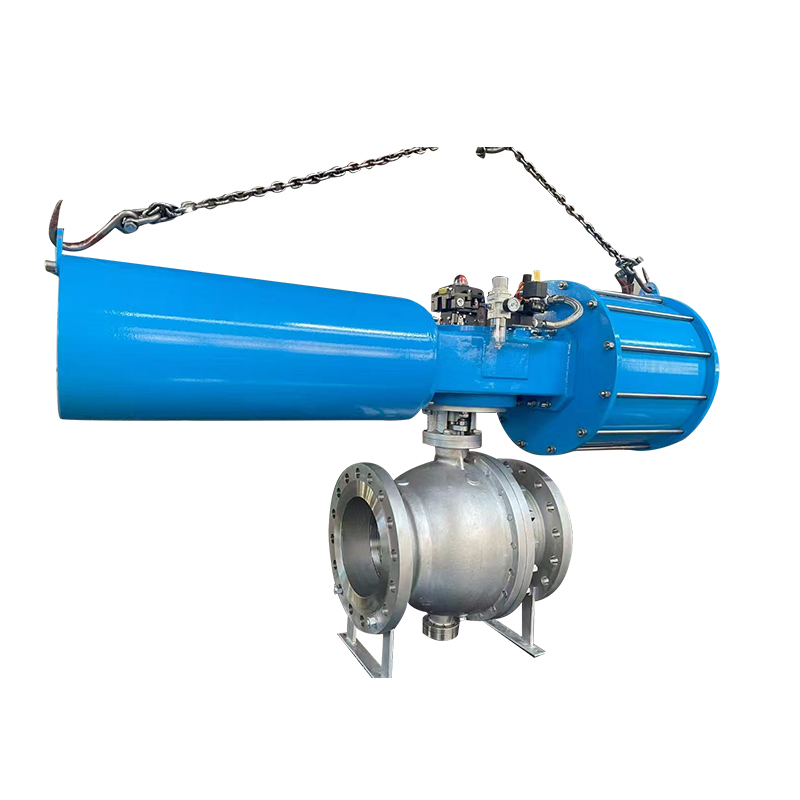
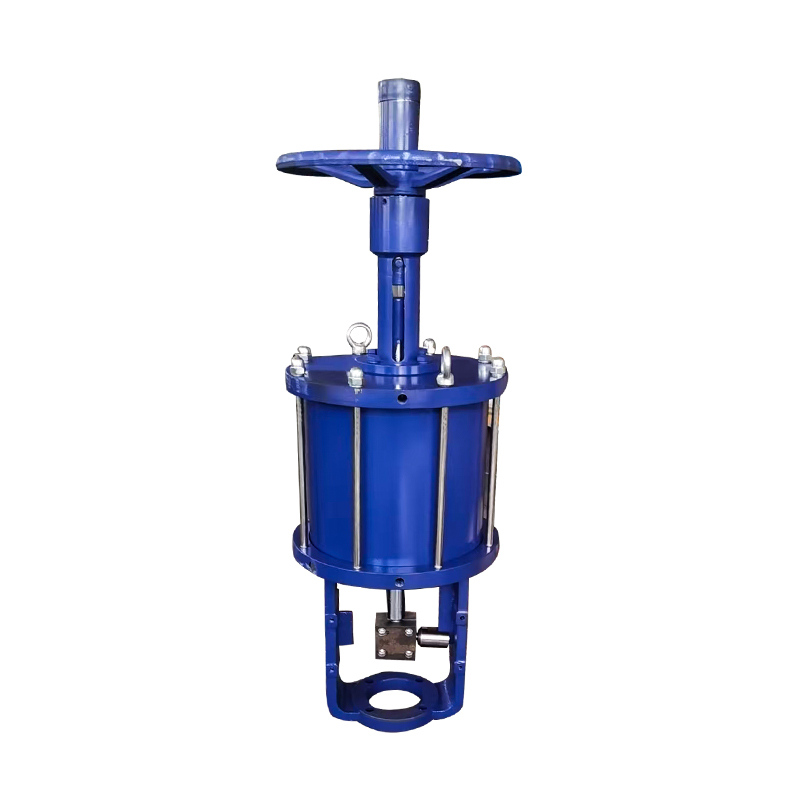
Scotch yoke actuators can be configured as either single-acting (spring-return) or double-acting (air-to-open and air-to-close), offering flexibility based on operational needs. Additionally, they are compatible with a wide range of valve sizes and can handle demanding service conditions, including high-pressure environments or systems with infrequent cycling.
Their robust construction, efficient torque output, and adaptability make Scotch yoke type actuators a common choice for many industrial valve automation systems.
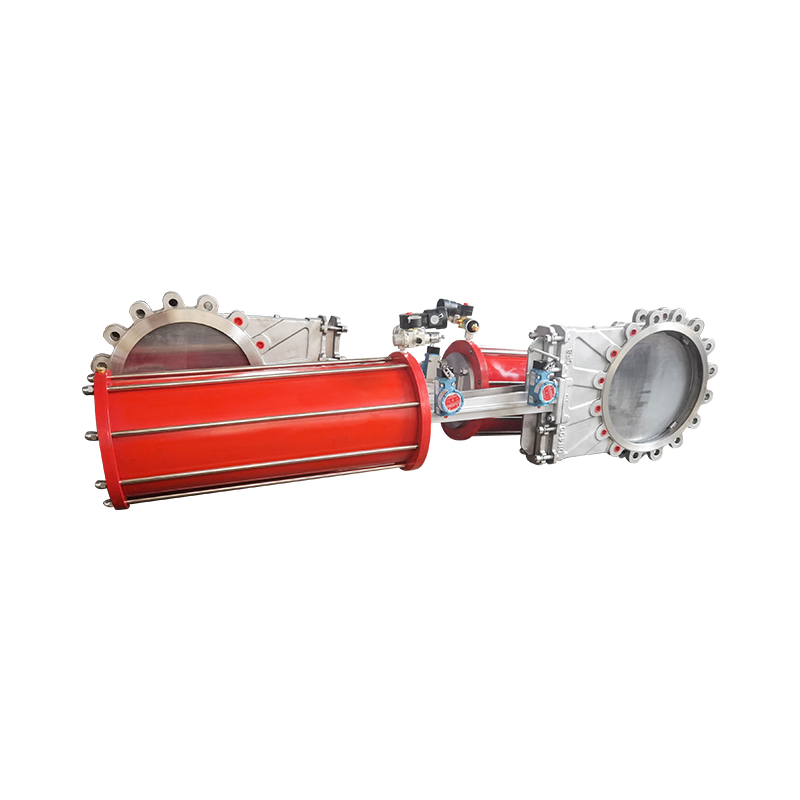
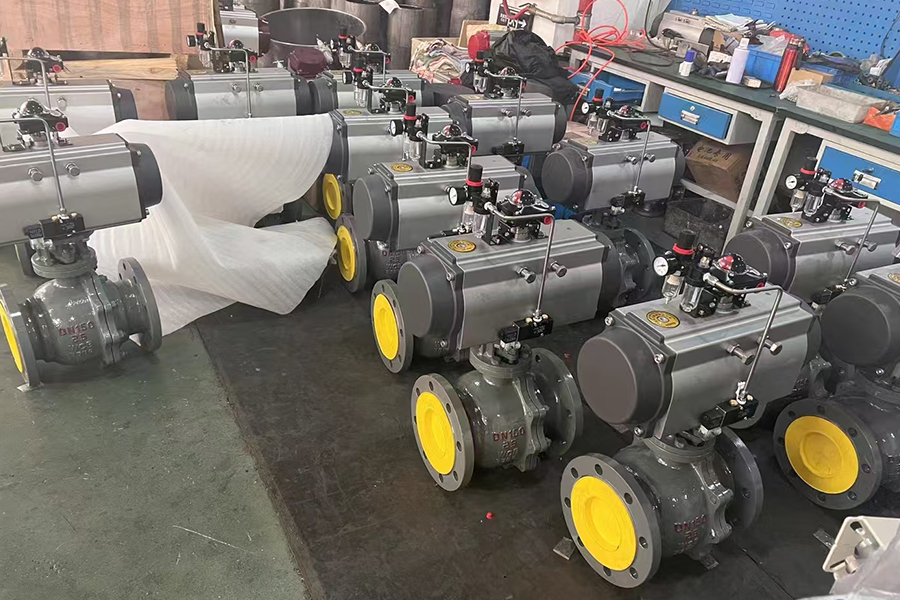
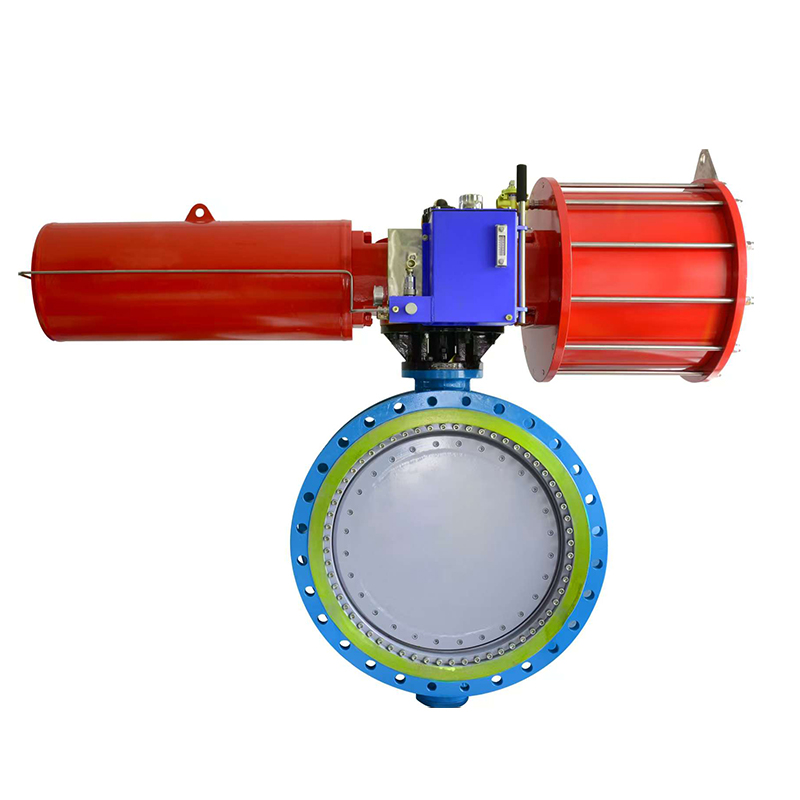
Linear pneumatic actuator valves are frequently used in industries where precise control of fluid flow is required, especially in systems that operate with linear valve motion such as globe, diaphragm, or gate valves. These actuators use compressed air to create straight-line motion, pushing or pulling a valve stem to open or close the valve.
One of the common application areas for linear pneumatic actuator valves is the process industry, which includes oil and gas, chemical production, and pharmaceuticals. In these sectors, accurate modulation of flow, pressure, or temperature is essential. Linear actuators are ideal for these applications due to their smooth and stable motion, which allows for fine adjustments to valve position.
In the water and wastewater treatment industry, linear pneumatic actuator valves are used to control the flow of water or chemical additives through treatment systems. Their ability to provide reliable and repeatable motion makes them suitable for continuous operation in environmental conditions that may be dusty, humid, or corrosive.
Another important application is in HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems, where linear pneumatic actuators are employed to regulate dampers and control air or fluid flow. Their fast response and compatibility with control systems make them suitable for maintaining stable climate conditions in large buildings or industrial facilities.
Additionally, food and beverage manufacturing frequently employs these actuators in processing and cleaning systems where hygiene and accuracy are vital. Stainless steel models of linear pneumatic actuators are often used in these cases to comply with sanitary standards.
Linear pneumatic actuator valves are valued for their simplicity, reliability, and ease of integration into automated control systems. Their widespread use across diverse sectors highlights their versatility and effectiveness in achieving precise linear motion in fluid handling operations.