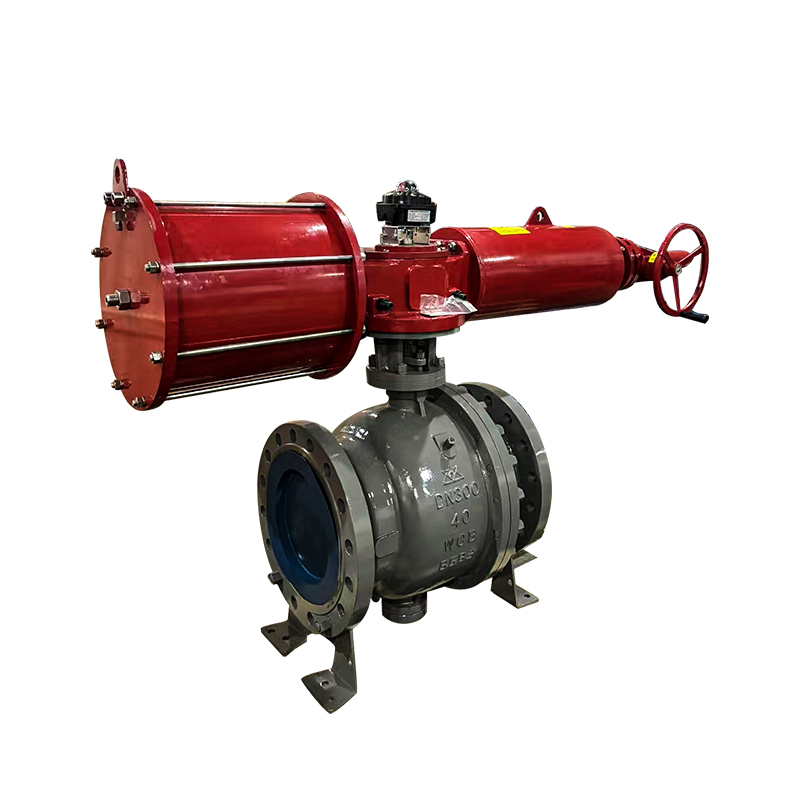
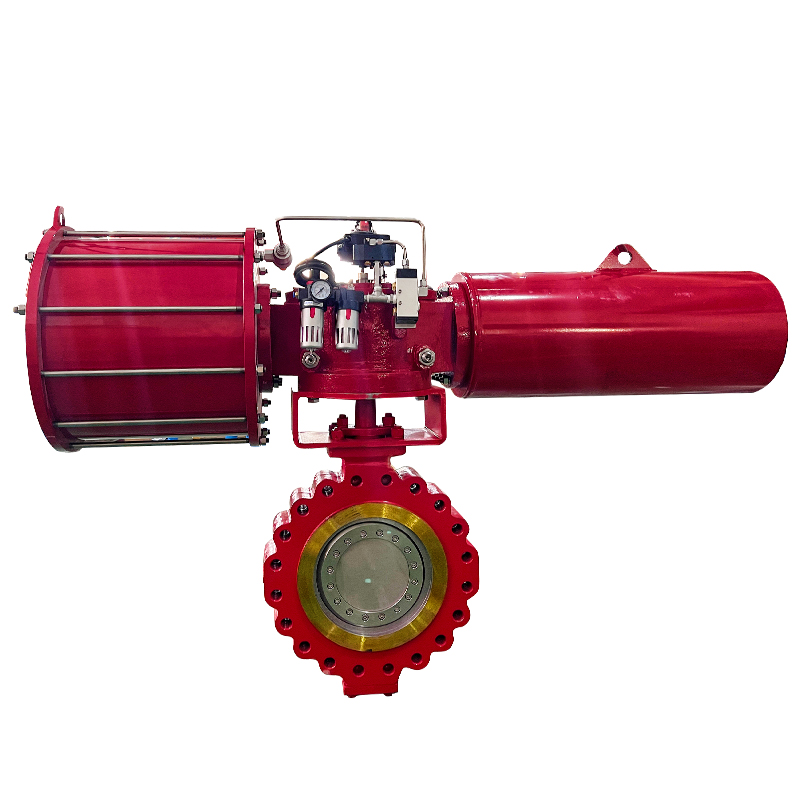
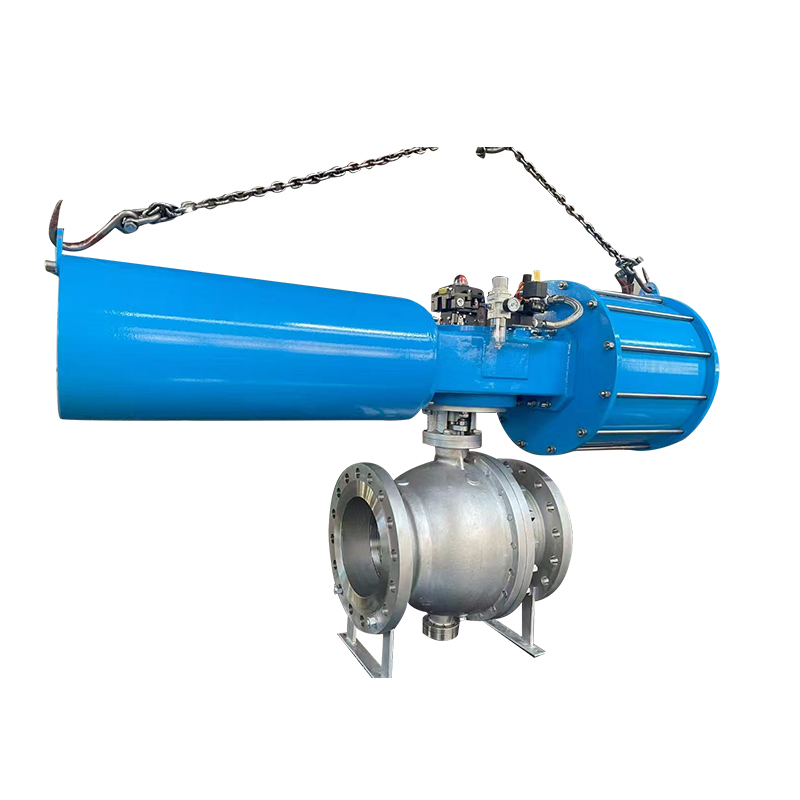
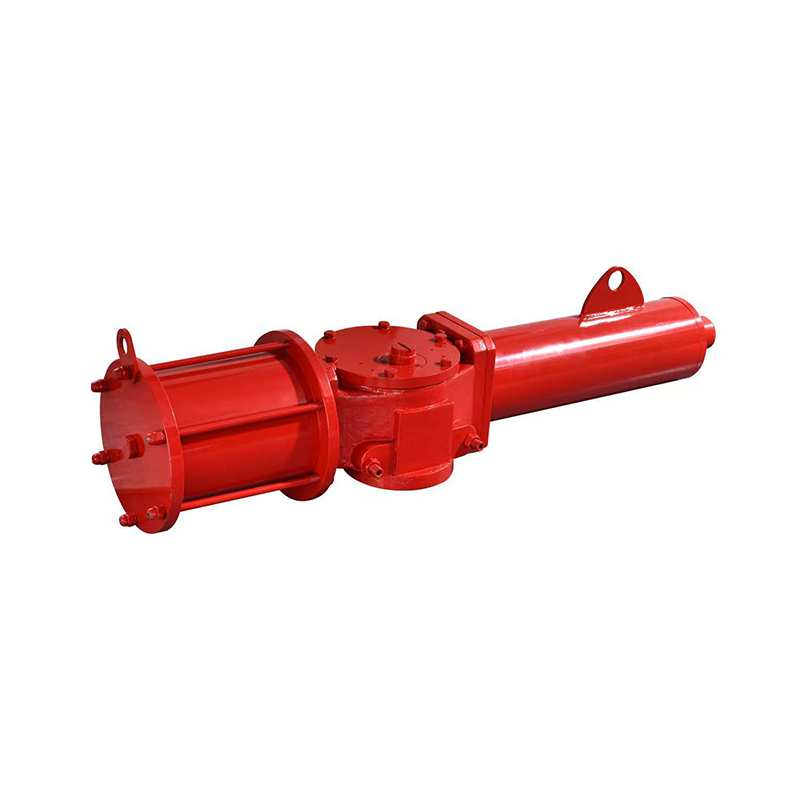
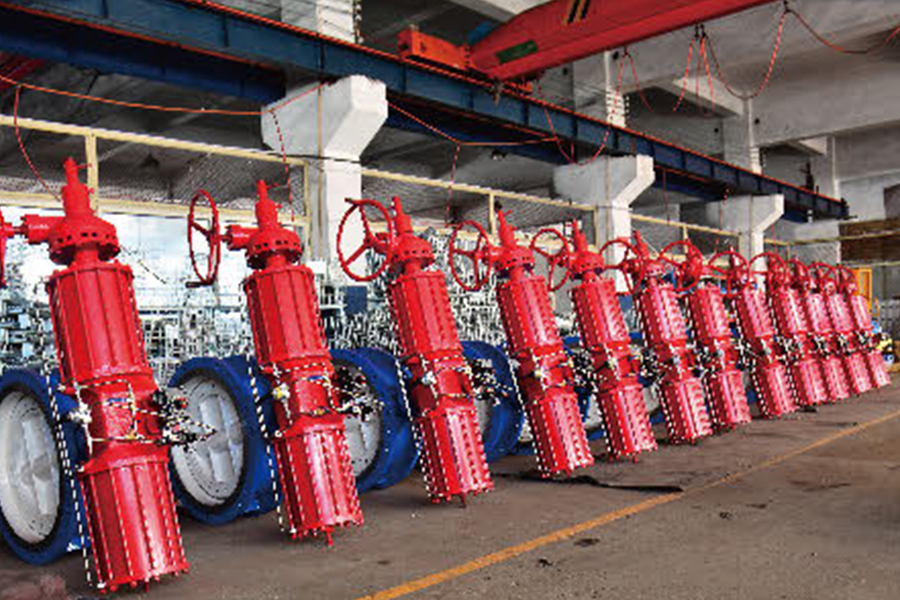
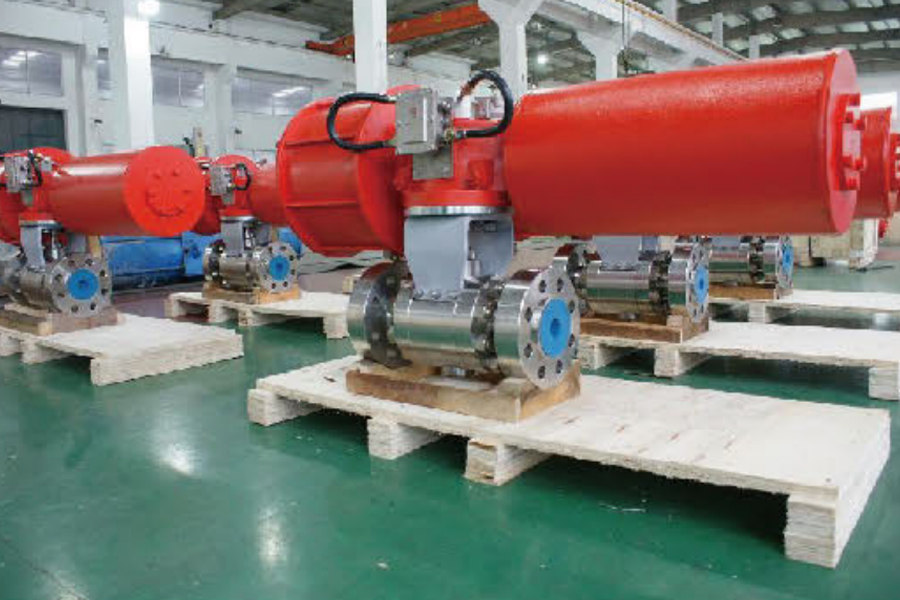
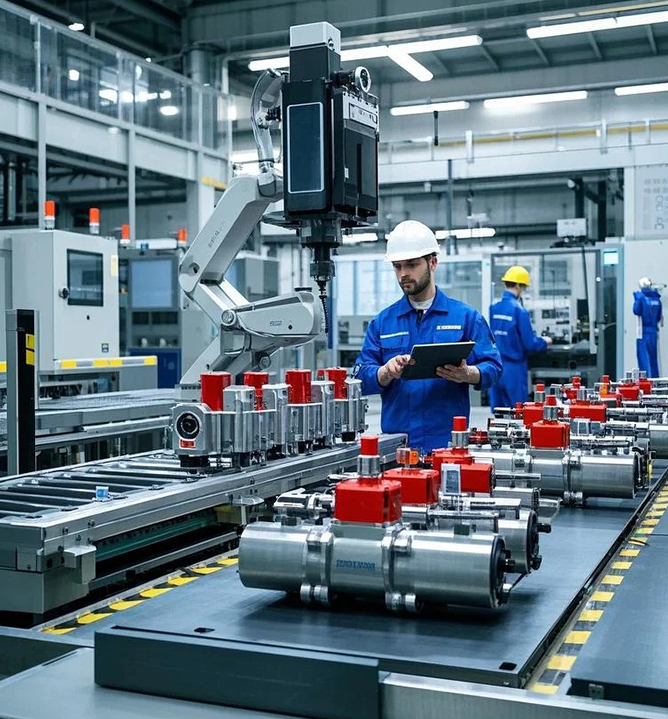
When choosing an automatic control valve, you need to consider multiple factors to ensure that it can meet the needs of the system and operate stably. Here are some key selection points:

1. Valve type and material
Type: Select the appropriate valve type according to the application scenario, such as ball valve, gate valve, stop valve, etc.
Material: Select the appropriate material according to the corrosiveness and cleanliness of the medium, such as cast iron, carbon steel, stainless steel, etc.
2. Strength and sealing performance
Strength: The valve must have sufficient strength and rigidity to withstand the pressure of the medium and avoid cracking or deformation.
Sealing performance: Ensure that the sealing parts of the valve can effectively prevent the leakage of the medium.
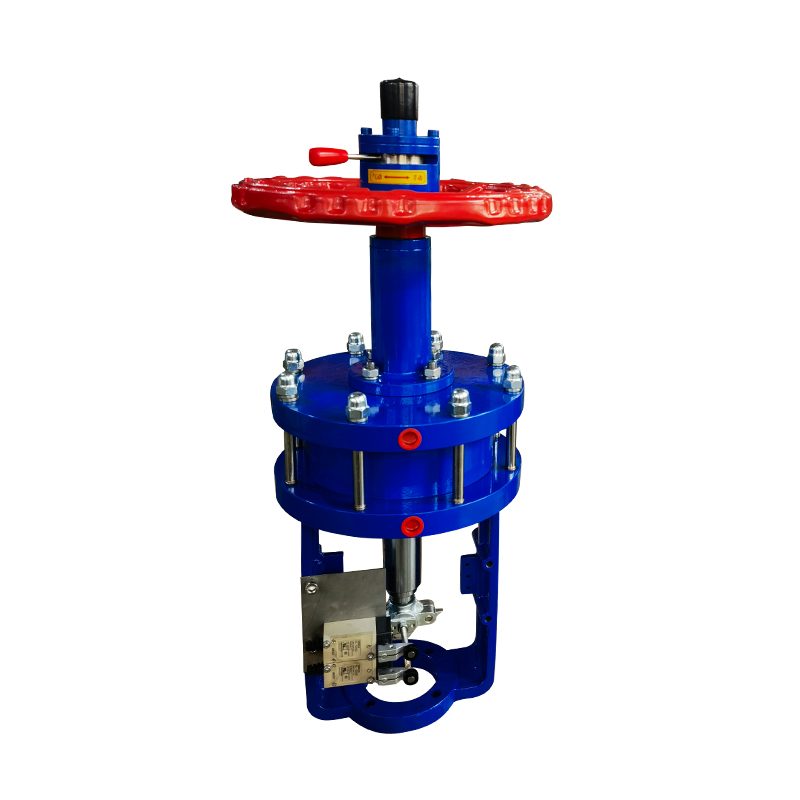
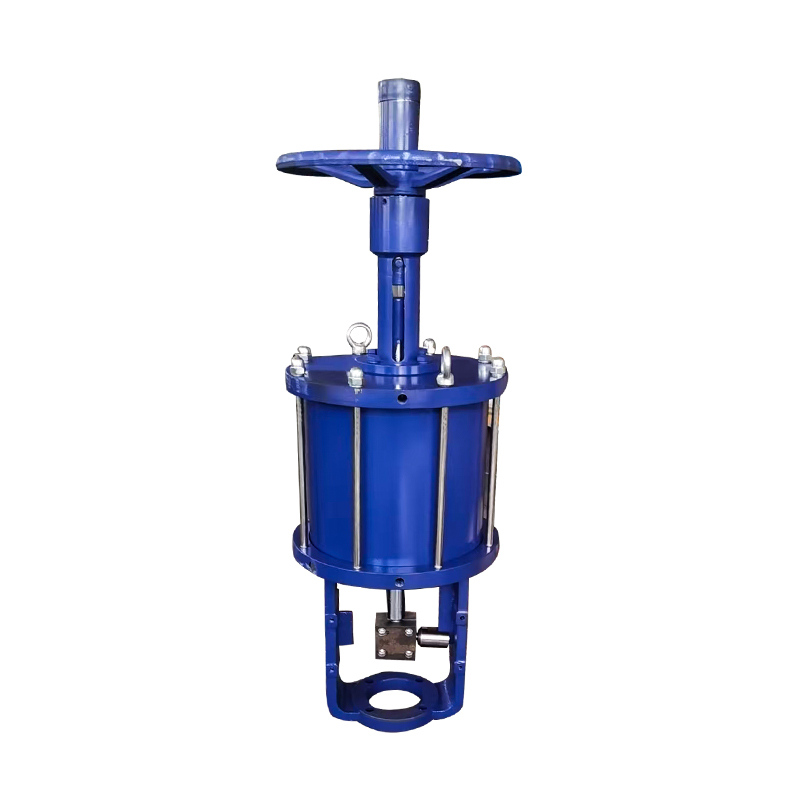
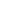
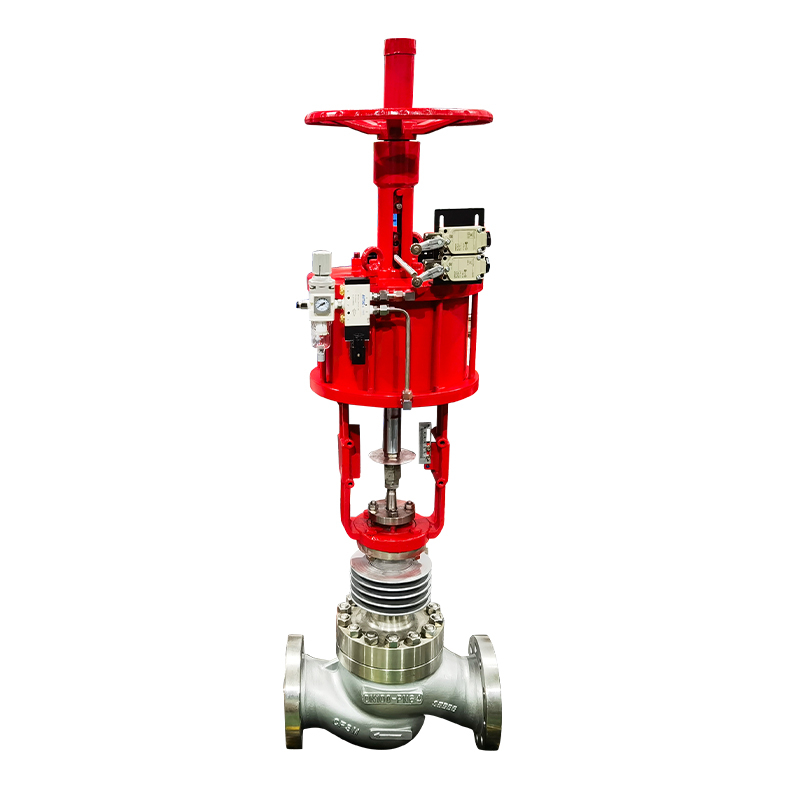
3. Control method and actuator
Control method: Select open or closed control method according to needs.
Actuator: Select the appropriate drive method (such as electric, pneumatic, hydraulic) and power to ensure that the valve can be accurately controlled.
4. Flow and pressure range
Flow characteristics: Select a valve with appropriate flow characteristics according to the system flow requirements.
Pressure range: Ensure that the rated pressure of the valve can meet the needs of the system.
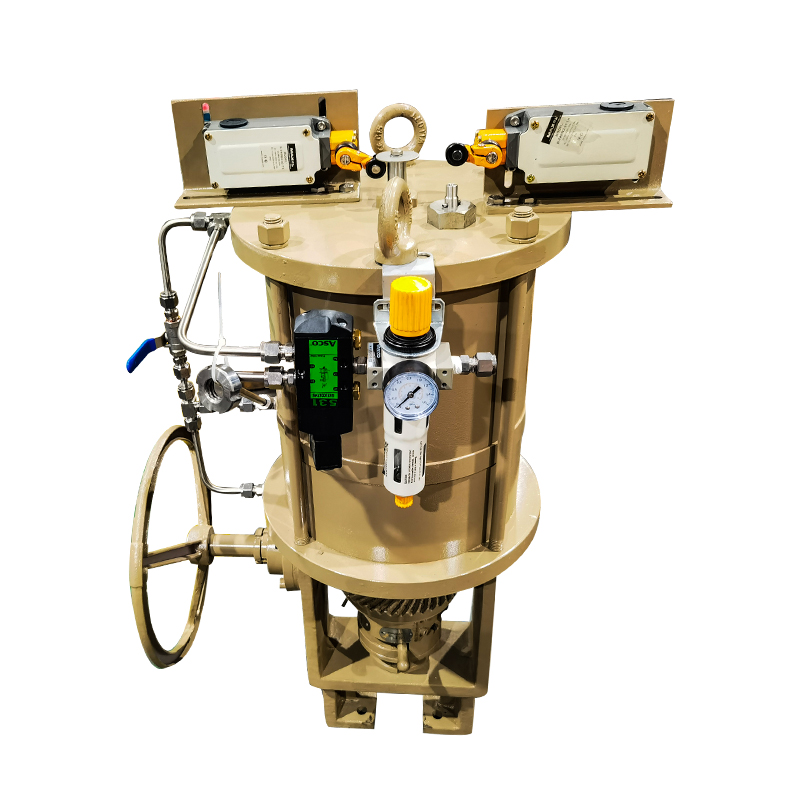
5. Accuracy and accessory configuration
Adjustment accuracy: Select valves with corresponding accuracy according to the system's requirements for control accuracy.
Accessory configuration: Consider whether filters, pressure reducing valves, limit switches and other accessories are needed to enhance system functions.
6. Brand and after-sales service
Brand: Choose a well-known brand to ensure product quality and after-sales service.
Supplier: Choose a professional supplier, require complete technical information, and understand its production process and quality management system.
7. Price and maintenance cost
Cost-effectiveness: Consider price and maintenance cost and choose valves with high cost-effectiveness while meeting performance requirements.
8. Special needs
Explosion-proof type: Suitable for occasions requiring explosion-proof.
Insulation jacket type: Suitable for special media and environments.
Through the comprehensive consideration of the above points, you can select an automatic control valve that meets the system requirements to ensure its stable and reliable operation.
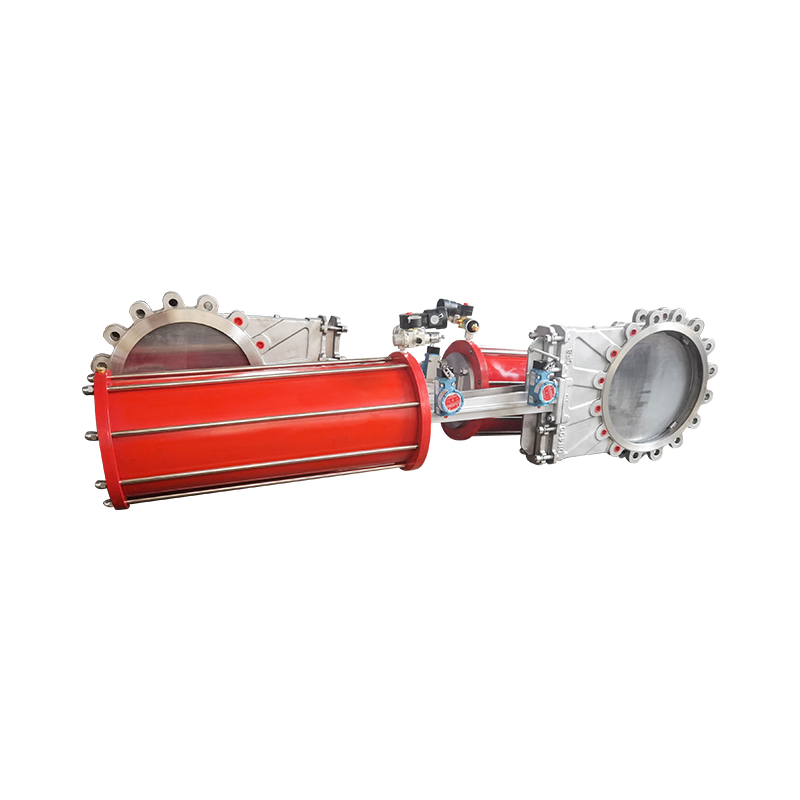
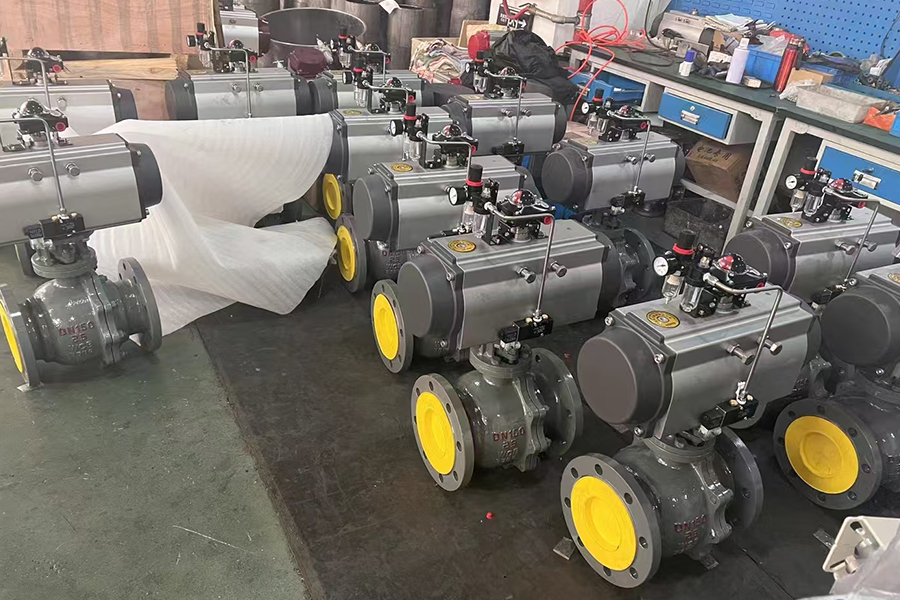
In industrial automation and fluid control systems, valves play a pivotal role in managing the flow of gases and liquids. Among the many types, air actuated ball valves and pneumatic flow control valves are widely used due to their efficiency, reliability, and ability to be integrated into automated systems. This article explores the different types of air actuated ball valves and outlines the key functions of pneumatic flow control valves, offering a clear overview for engineers, technicians, and facility managers.
Air actuated ball valves, also referred to as pneumatic ball valves, use compressed air to open or close a ball-shaped closure mechanism within the valve. They are commonly used in industries requiring fast, reliable on/off control of flow.
These valves operate with a single air line and a spring mechanism. When air pressure is applied, the actuator moves the ball to the open or closed position. Upon releasing the pressure, the internal spring returns the valve to its original position. This type is advantageous in applications where a fail-safe mechanism is required, ensuring the valve returns to a default position during power or air failure.
Double-acting valves require air pressure to both open and close the valve. They provide more control and force in operation compared to single-acting models. These are typically used in applications where speed and precision are critical, or where fail-safe conditions are not a priority.
Air actuated ball valves are available in 2-way and 3-way designs. A 2-way valve allows fluid to flow in a straight path from inlet to outlet, suitable for simple on/off applications. A 3-way valve has an additional port and can be used to divert flow between different paths, often used in mixing or diverting systems.
Pneumatic flow control valves are essential components in systems using compressed air to perform mechanical work. They regulate the rate of airflow, ensuring that actuators operate at the desired speed and efficiency. Here are the core functions and applications of these valves:
One of the primary functions of a pneumatic flow control valve is to manage the speed of pneumatic cylinders or actuators. By adjusting the flow rate of air entering or exiting the actuator, the valve ensures consistent and controlled movement. This is especially important in automated systems where timing and precision are critical.
Flow control valves help in reducing sudden pressure changes that can cause shock loads or erratic movements in pneumatic systems. By providing a controlled flow, they contribute to system stability and minimize wear on components.
While not their main function, some flow control valves are integrated with directional valves to manage both the direction and rate of airflow. This combination enhances the performance of more complex pneumatic circuits, such as those found in packaging or assembly equipment.